Sustainable living is one of the top trends these past few years. One of its main principles is enriching mother earth and producing your food. Now, it’s about time to learn how to grow sugar cane and make your sugar at home.
Does it sound intimidating to create sugar at home?
Well, it’s easier than you think. If you have the patience and the will of a true gardener, you will definitely enjoy the process of planting sugarcane and making your sugar syrup.
(You could use the table of contents below to jump to the sections that are most important to you.)
How To Grow Sugar Cane At Home
You can grow sugar canes from their stem or ratoons that have already sprouted from an old sugar cane stem.
Here are the materials you’ll need to plant your sugar canes at home:
Materials:
- 1 Spade
- 1 Machete or saw
- 1 Shovel
- A bucket of compost
- 1 Deep and wide container or garden bed
#1 Choose a 1-foot long sugar cane stem or a ratoon
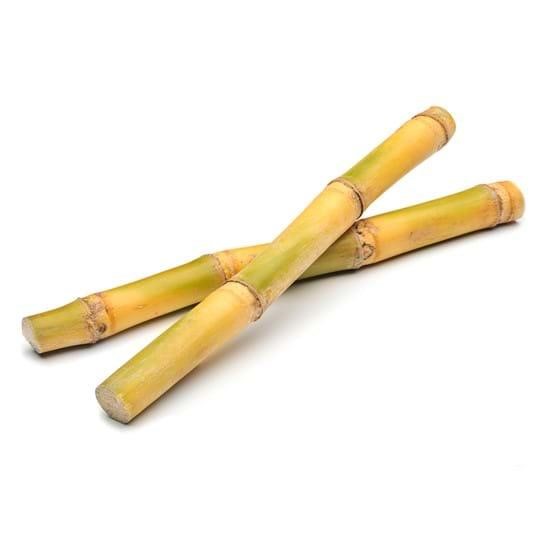

Sugar cane grows and develops roots in their joints. You can either buy freshly cut sugarcane from a farmer’s market or a local farm in your area.
Another way is to use a ratoon which is a sprout from an old sugar cane. Choose canes that have white and clean tissues and don’t have any signs of rot or diseases.
#2 Create a furrow or fill a deep and wide bucket with fertile soil

The ideal location for planting a sugar cane is in a sunny area where they can receive 6 to 8 hours of sunlight.
If you choose to grow your sugar canes in a pot, make sure to select a deep bucket that can hold high stalks of sugar canes.
#3 Add compost and water the soil
As you fill in the bucket or build the furrow, make sure to mix in a handful of compost for every cutting.
Compost helps the soil to be more nutrient-dense and well-draining. Check the soil drainage by watering the furrow and the bucket and see if the water drains properly.
To check if the soil has good drainage after the first batch of watering, pour another round of water in the furrow. The ideal drainage rate is 1 inch per hour.
If the water level doesn’t change after an hour, the soil is too compact and may cause the roots to rot or drown. If the water drains too fast, the inground soil or potting soil has poor water retention that may cause drought stress on plants.
#4 Plant the sugar canes or ratoons
Measure the furrow and plant the sugar cane cuttings six feet apart. If you have ratoons, plant them at least 1 foot apart.
Sugar canes are planted horizontally, so make sure to add adequate space for every cutting. Planting the cuttings in a vertical pattern will prevent the nodes or joints from touching the soil.

In some cases, gardeners place the sugar cane cuttings in a pail of water where the joints are submerged.
After six weeks, the roots will start to grow and become ready for transplanting. However, there is a high chance that the cane may rot if you fail to remove them from the water in time.
#5 Fertilize and weed your sugar canes
Growing a sugar cane takes about a year to mature. The longer you wait to harvest them, the sweeter they can be. As the stem and leaves start sprouting from the soil, you can continue adding compost or apply nitrogen-rich fertilizer.
Also, check on the weeds that grow around your sugar canes. Adding mulch can help prevent the weeds from growing and keep the soil moist, especially during spring and summer.
#6 Harvest your first sugar cane at home
If you live in a warmer region, you can extend the harvest time to October so you can enjoy a sweeter sugar cane juice.
However, if you live in a colder area, you must harvest the sugar canes in September. Once the frost starts, you may never be able to have a good quality of sugar canes.
The bamboo-like stems of sugar canes are sturdy and require a more durable tool like a saw or a machete. Be careful in using the machete to avoid hurting yourself.
Getting To Know Sugar Canes
Sugar cane is a type of grass that grows stems as wide and tall as bamboo. It is a tropical plant that grows well in warm temperatures.
Sugar canes are commercially grown and contribute to 75% of sugar produced around the globe.
Aside from a sugar source, sugarcanes are also the leading source of ethanol. Countries like Brazil are using ethanol to produce biofuel like biodiesel in the country.
In Brazil alone, 665 million metric tons of sugar canes are produced to sustain the demand for both sugar and biofuel.
Sugar canes are also cultivated for other products like molasses and rum. Molasses are the sweet black syrup which is a by-product of sugar production.
The waste materials from juicing sugar canes are also used as pet food and other biodegradable products.
Sugar cane takes a year to grow. It can overwinter and continue growing until the next spring. It can grow up to 20 feet high and 2 to 4 inches in diameter.
The best time to plant sugar canes is during late summer, and the harvest time would be in the next summer.
To help you grow the best quality of sugar canes, you must give them the ideal environment where they can thrive.
Here are the best conditions for your sugar canes:
Temperature and Weather Requirements
Sugar canes grow well in Zones 9 and Zone 10. In warm areas, it can grow throughout the year.
The minimum temperature required for the growth of sugarcane is 20°C (68 °F), and the ideal temperature is around 90-100°F. They need full sun exposure to grow strong and bigger stems.
If you happen to live in a colder region, your sugar cane will only be good as an annual. They can’t tolerate the cold, and you must bring them indoors during winter to keep them growing.
So, before you decide on planting them, you must have a space inside your house for large plant bends of sugar canes.
Soil Requirements
The best soil for sugarcane is fertile soil with clay soil, sand, and compost materials. However, they can be pretty versatile and grow on clay, sandy, or loam soil. It is also not too sensitive when it comes to acidity.
You can plant it with a soil PH level of 5 to 8.5.
Applying mulch can also be beneficial in keeping the soil moist. It can also help keep the weeds away and help your sugar canes grow without competing for the soil nutrients.
Water Requirements
Sugar canes love moist soil and need about 1 to 2 inches of water every week. If you are in a region with a lot of rainfall, you may lessen your watering routine to avoid drowning the roots.
In preparation for harvest time, you should stop watering them. Halting the irrigation allows the sugar cane to produce more sugar on its stem.
This method allows most of the juicy sugar sap above the ground, letting you harvest a much sweeter batch of sugar cane juice.
Fertilization
Sugar canes require more nitrogen and phosphorus to grow bigger and stronger stems.
Though general fertilizers like 14-14-14 can help, you may benefit more from fertilizers with higher nitrogen content or the first number from the fertilizer ratio.
You may use the following fertilizers with high nitrogen content:
- Dr. Earth Organic Fruit Tree Fertilizer
- Miracle-Gro All-Purpose Plant Food
- Espoma Tree Tone Fertilizer
As you fertilize your sugar canes, make sure that you are not overfertilizing them. Too much nitrogen can cause the stems to weaken and affect the quality of the sugar produced.
Pest And Disease Control
Sugar canes are also not an exemption when it comes to pest damage. They may have bamboo-like coverings, but they can also get damaged by persistent pests and diseases.
As preventive care, you can apply neem oil and diatomaceous earth to keep the pesky bugs at bay.
Here are the common diseases that may damage your growing sugar cane stems:
Diseases
(1) Mosaic virus is a virus that causes white, green, or red spots on foliage. It can also cause leaf curling which can affect the photosynthesis in sugar cane plants. It is often spread by pests that damage your plants.

(2) Red rot is a plant disease that causes white and red patches and an alcoholic smell inside the stems of sugar canes.
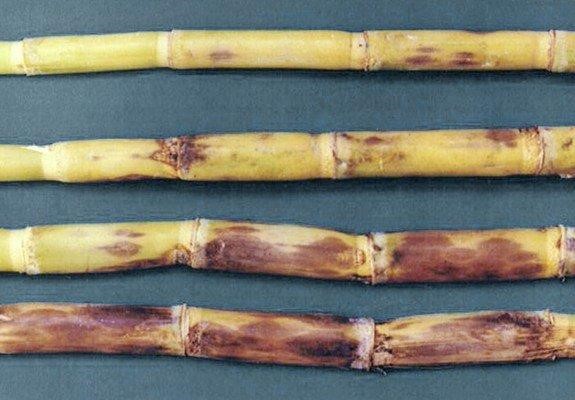
The first manifestation of this disease is when the leaves start to yellow, and red patches start to show on the sugarcane stems.
If left untreated, the sugarcane will eventually rot from the inside and die.
(3) Gumming disease is a disease caused by Xanthomonas vasculorum. Signs of infection include discoloration of leaves with necrotic areas. The stems are oozing and have discoloration and rotting spots.

(4) Sugarcane eyespot is a minor disease in sugar canes where the leaves develop circular spots with reddish-brown linings. These spots are caused by the toxin produced by the eyespot.
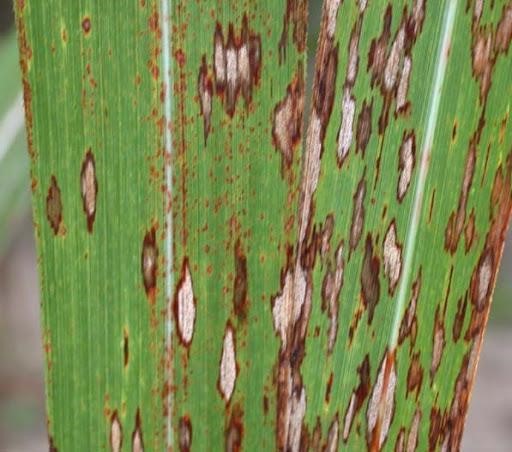

Pests
(1) Sugarcane moth borers are detrimental to sugar canes if they develop in numbers. The larval stage of this insect can pierce through the stalks of sugar canes.
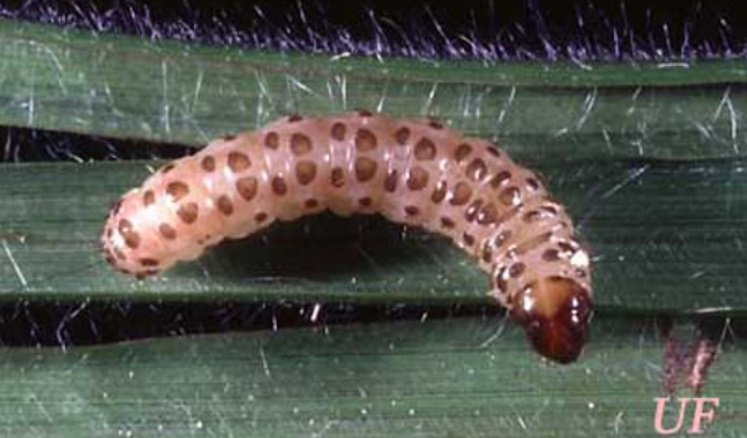

If left untreated, the new leaves and mature tops can die. It will also affect the quality of the sugar cane juice extracted from the stem.
(2) Sugarcane leafhoppers are one of the major pests in sugar canes that are common in grass plant species. They suck on the sweet sap from sugar canes, causing tiny holes in the leaves and stems.
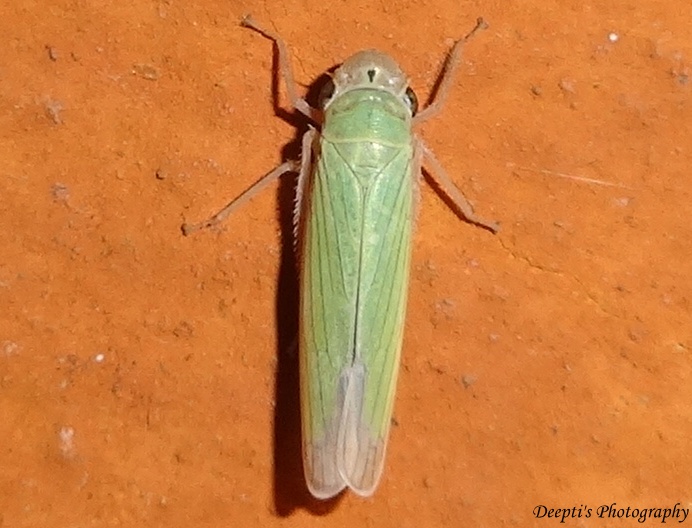

(3) Rats are one of the potential pests of sugar canes grown in residential areas.
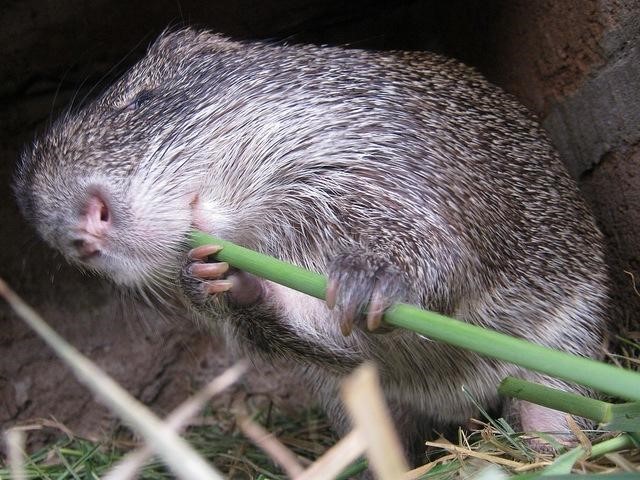

Since rats frequent neighborhoods and sewers, they can most likely target your sweet sugar canes. They will chew on the rind of the sugar cane and munch on the juicy tissues of the sugarcane.
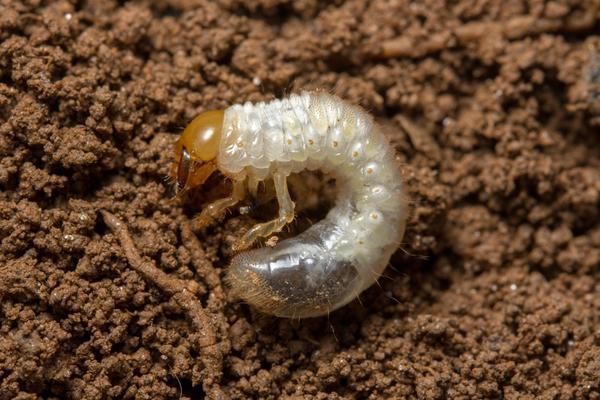
(4) Sugarcane white grub is the larvae of a beetle that lives underground. It grows in the soil and feeds on the roots of sugar cane. It is a notorious root-eater that also damages other crops like pineapples and strawberries.

How To Make Sugarcane Syrup At Home
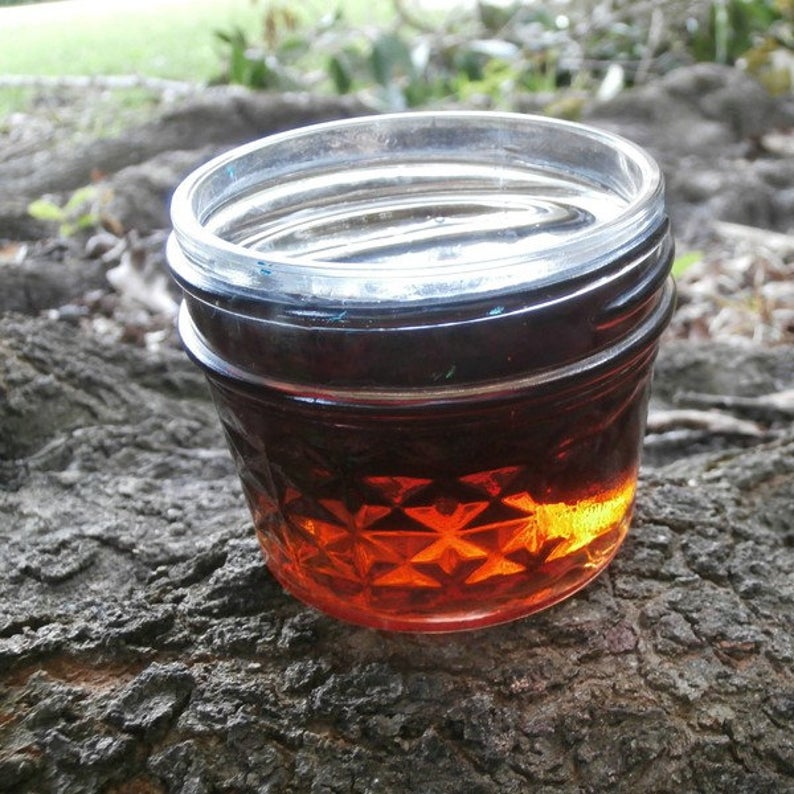

If you’re wondering how you can extract the syrup or sugar from the sugar cane, you can either do it manually or extract the juice with a pressing machine.
However, the juice press is rare and can only be found in juice shops or commercial farms.
The good thing is you can do the manual extraction by boiling the harvested sugar canes.
Here’s how:
- Clean the sugar canes by removing their outer layer. Brush the white fibers of sugar cane and remove any debris or dust.
- Fill a large pot with water and place the cleaned sugar canes. Make sure that they are submerged in the water.
- Boil the sugar canes for 4 hours to extract their sweet juices.
- Remove the sugar canes from the pot and filter the juice using a strainer.
- To turn the sugarcane juice into syrup, boil it for another 2 hours until the syrup thickens. You have to keep stirring it to achieve a well-cooked syrup.
- Once the syrup has been formed, let it cool before transferring it to a container.
- Transfer the syrup to a clean airtight jar and keep it in the refrigerator. The sugar syrup can last for up to two weeks.
Final Thoughts
There’s a different kind of fulfillment when you successfully grow your food. You find more value in it and try to savor every bite and appreciate your food better.
We hope that you will have a smooth growing journey with your sugar canes.
Did you find this post helpful?
Please share this post with your friends, and let us build a more sustainable community and take advantage of the piece of land we have at home.
Planting sugarcanes is more than just about sustainable living. It is also about helping Mother Earth by growing more plants.

Can the cane syrup be cryopackaged and stored in a freezer?
Hi Donita, Pure cane syrup doesn’t spoil and is kept in a cool spot no refrigeration will keep a long time.